How to Choose The Best Yogurt
Apr 25, 2023
Choosing between all of the yogurt options at the grocery store can be confusing. Our dietitian-approved guide to choosing yogurt is intended to help you determine the best yogurt for your goals! If you'd like to learn more, listen to our Podcast episode here where the dietitians of Vitality Nutrition discuss their unique perspectives on yogurt and what to consider for your specific goals!
Go For Protein!
As Registered Dietitians, we typically recommend yogurt as a high-protein food to build into meals and snacks. Dairy based yogurts such as Greek yogurt and Skyr yogurt will be high in protein and regular dairy-yogurt or plant-based options like coconut or oat yogurt will be lower in protein. We recommend reviewing Nutrition Facts tables to choose yogurts with >15g of protein per serving if you are choosing to purchase yogurt as a protein source.
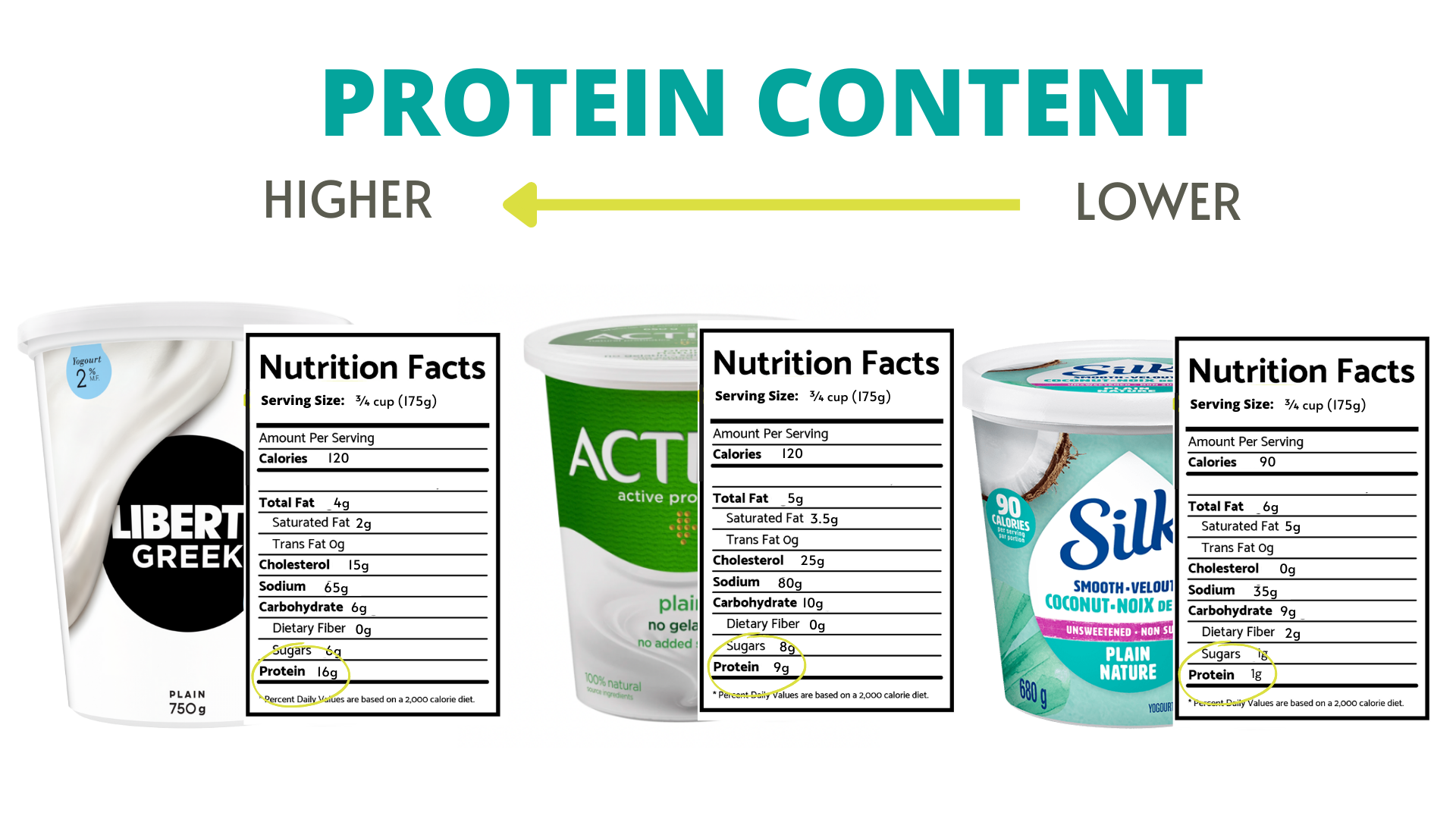
NOTE: While as dietitians we recommend choosing a higher protein option, we understand that choosing the lower protein yogurt choice (eg. coconut yogurt) may be warranted when navigating an allergy, intolerance, or preference for plant-based eating.
High Fat or Low Fat?
Dairy-based yogurt can be lower fat (0-2% milk fat) or higher fat (4-10% milk fat). The "MF" on the label stands for "milk fat" and represents the percentage of fat contained in the product. In the past, nutrition institutes recommended low-fat dairy to prevent heart disease. However, it is now understood that the fat from dairy foods can have a neutral or positive effect on cardiovascular health (source). For that reason, our team of Registered Dietitians does not recommend avoiding higher-fat dairy products including yogurt.
That being said, a higher fat dairy-based yogurt will have less protein as the fat in the yogurt displaces the protein content. If you are choosing a dairy-based yogurt as a protein choice, our team of dietitians recommends choosing a yogurt with <5% milk fat (MF) as this will ensure the yogurt still has >15g of protein. However, you may decide to choose a higher fat yogurt product in consideration that you are using it as a source of fat in your diet rather than a significant source of protein.
Review the Nutrition Facts table below that compares the protein content of a 2%MF yogurt to a 10% MF yogurt. The 2% MF Greek yogurt has the most protein per serving which is the ideal choice if you are choosing a yogurt to boost your daily protein intake! If you are looking to boost your fat and calorie intake then the 10% MF yogurt may be ideal from a nutrition standpoint.

Consider Added Sugars
Yogurt contains naturally occurring sugars (ie. lactose) and flavoured yogurt varieties contain added sugars to enhance the sweetness and flavour.
If you are comparing Nutrition Facts tables for yogurt you will notice that even plain yogurt has some sugar listed which is the lactose naturally found in the dairy. Yogurts with added sugars will contain a higher count of sugar on the Nutrition Facts table.

Many benefit from reducing added sugars in their diet. For some, this may mean choosing a plain yogurt that does not contain any added sugar. That being said, plain varieties of yogurt can be tart and bland. As Registered Dietitians, we recommend boosting the flavour of a plain yogurt to enhance enjoyment! Some ideas:
- Add fresh or frozen fruit. Frozen or fresh berries or fruit add natural sweetness to the yogurt alongside a boost of fibre, vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants!
- Mix in flavoured protein powder. Many of our nutrition coaching clients enjoy mixing a flavoured protein powder into their plain yogurt. This enhances the flavour and adds an additional boost of protein to the yogurt. We share a recipe here.
- Combine plain and flavoured yogurt. If you are looking to reduce added sugar but aren’t onboard for the tart flavour of plain yogurt then you may consider mixing a flavoured yogurt with a plain yogurt. This reduces the added sugars but still adds some sweetness to enhance the flavour!
- Choose a flavoured yogurt with less added sugar. Some yogurt varieties (eg. Skyr yogurt) will contain less added sugar than other yogurt varieties (eg. Greek yogurt). Compare Nutrition Facts tables to choose a yogurt with less added sugar.
- Sweeten on your own. Purchase plain yogurt and add your own sweetness with a drizzle of honey or maple syrup. Honey and maple syrup are still forms of added sugar but by purchasing the plain you can control the amount of sugar you add!
- Create a savoury dip. Turn your plain Greek yogurt into homemade tzatziki or mix-in spices like ranch seasoning to create a dip for vegetables.
On the other hand, there are circumstances where you may intentionally choose a yogurt with added sugar based on your unique goals and preferences. For example:
- Perhaps choosing a flavoured yogurt means you will enjoy consuming the yogurt and therefore reach your protein and calcium requirements.
- Perhaps your goal is to gain weight or increase your caloric intake and choosing a yogurt with added sugar helps to reach your total energy requirements
While reducing added sugars is a helpful nutrition goal for many, it is important to consider your personal goals and whether flavoured yogurt could be a beneficial strategy to meet your energy, protein, and calcium requirements!
Is Plant-Based Better?
A rise in plant-based eating has brought a variety of new yogurts to the scene including non-dairy yogurts like coconut or oat milk yogurt. Of course, if you have decided to consume a plant-based diet or have an intolerance or allergy to dairy then plant-based forms of non-dairy yogurts will be preferred. However, as Registered Dietitians, we believe it is important to highlight that just because a product is labeled “plant-based” doesn’t mean it is best for your goals. Dairy-based yogurts offer protein and naturally occurring calcium, potassium, B12, phosphorus, and more which are important nutrients to consume enough of.
Lactose-Free
Many people have an intolerance to lactose meaning they can not efficiently break down and absorb the natural lactose sugar found in dairy products like yogurt. The undigested lactose ferments in the gut causing a collection of digestive symptoms including bloating, gassiness, and diarrhea. Some varieties of dairy-based yogurt like Greek or Skyr yogurt naturally contain less lactose compared to other milk products due to straining in the production processes.
Manufacturers also create “lactose-free” versions of dairy yogurt by adding the lactase enzyme to the product. Those with a lactose-intolerance may find the added lactase enzyme allows them to enjoy dairy-based yogurts without digestive symptoms.
Additional Nutrition Benefits
Both dairy and non-dairy yogurt will contain probiotics that may assist in gut health alongside naturally occurring or fortified vitamins and minerals like calcium, vitamin D, vitamin A, and vitamin B12. If choosing a plant-based yogurt we recommend ensuring calcium has been added to the product to help you reach your daily calcium requirements.
Dietitians Top Ways to Enjoy Yogurt
Some ways to incorporate yogurt into your recipes, meals, and snacks include:
- Use it as a base for a yogurt parfait for breakfast or a snack
- Incorporate Greek yogurt into high protein Greek yogurt waffles
- Mix yogurt into overnight oats
- Add a scoop of yogurt to a smoothie to boost the protein content
- Make a savoury dip like tzatziki or creamy guacamole to dip vegetables
- Use yogurt to replace the oil or butter in your muffin recipes
- Make frozen yogurt bars for breakfast or a wholesome dessert
Bottom-line
Choosing a yogurt depends on your personal preferences, tolerances, and goals. As Registered Dietitians, we find ourselves recommending 0-4% M.F. plain Greek or Skyr yogurt most often as it is a versatile ingredient that is high protein, low in added sugars, and rich in key micronutrients like calcium.
Listen to our Podcast episode here for a full discussion on choosing the best yogurt for your goals!
Ready to bring the evidence-based nutrition support of our Registered Dietitians into your kitchen?
Hungry for more?
Get recipes, tips, and updates from the Vitality Nutrition team straight to your inbox!
Don't worry, your information won't be shared.


